Sistem GPRS (General Packet Radio Services) digunakan oleh GSM Mobile phones, Sistem telepon mobile terpopuler di dunia (sejak 2004), untuk transmisi Packet IP. GPRS Core Network adalah bagian terpusat dari sistem GPRS yang juga mendukung jaringan WCDMA berbasis 3G. GPRS Core Network adalah bagian yang terintegrasi dengan GSM Core Network.
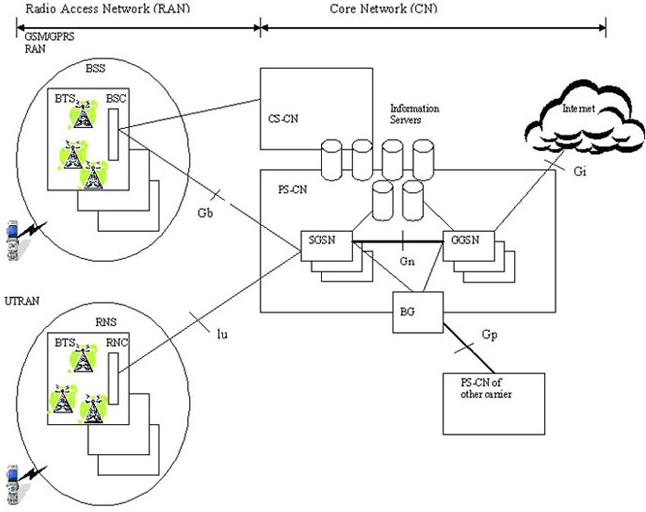
GPRS Core Network menyediakan mobility management, session management dan transport untuk paket Internet Protocol (IP) pada jaringan GSM dan WCDMA. Core network juga mendukung fungsi-fungsi tambahan seperti charging dan lawful interception.
Seperti GSM, GPRS adalah sistem open standards dengan badan standarisasinya disebut 3GPP.
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP)
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol merupakan protokol yang melewatkan IP dari SGSN ke GGSN pada GPRS core network. GTP adalah protokol yang memungkinkan end users dari GSM atau WCDMA berpindah dari satu tempat ke tempat lain dengan tetap tersambung ke internet dengan koneksi dari lokasi ke Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN). GTP melewatkan data subscriber melalui Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) ke GGSN yang menghandle session subscribers. GTP yang digunakan oleh GPRS core network adalah sebagai berikut :
GTP-U digunakan untuk transfer “user data” dengan “tunnel” terpisah untuk tiap PDP context
GTP-C digunakan untuk control:
- setup dan penghapusan PDP contexts
- verifikasi untuk GSN reachability
- updates, seperti: pergerakan subscribers dari satu SGSN ke SGSN lain
GTP’ untuk transfer “charging data” dari GSN ke “charging function“.
GGSN dan SGSN (keduanya disebut GSN) menerima pesan GTP-C (GTP-C messages) dengan UDP port 2123 dan GTP-U messages pada port 2152. Komunikasi ini berlangsung dalam single network atau bisa juga international roaming, yang dapat terjadi melalui GPRS Roaming Exchange (GRX).
“Charging Gateway Function” (CGF) menerima pesan GTP'(GTP’ messages) yang dikirim dari GSN dengan UDP port 3386. Core Network mengirimkan informasi “charging” ke CGF, termasuk waktu aktivasi “PDP context” dan kuantitas/quantity data end users yang telah ditransfer melalui core netwok.
GPRS Support Nodes (GSN)
GSN adalah network node yang mendukung GPRS pada GSM core network. Semua GSN harus mempunyai interface Gn dan support GPRS tunnelling protocol (GTP). Terdapat 2 jenis GSN, yaitu GGSN & SGSN.
GGSN – Gateway GPRS Support Node
Gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) berfungsi sebagai interface antara GPRS backbone network dan external packet data networks (radio network & IP network). GGSN mengkonversi GPRS packets dari SGSN ke packet data protocol (PDP) format yang sesuai (IP atau X.25) dan kemudian meneruskannya ke packet data network. Sebaliknya PDP address dari incoming data packets dikonversi ke GSM address untuk mobile user. “Re-address packets” dikirimkan ke responsible SGSN. Dalam hal ini, GGSN menyimpan current SGSN address dari user dan profile-nya di location register. GGSN bertanggung jawab memberikan alamat IP dan berperan sebagai “default router” yang menghubungkan UE (User Equipment). GGSN juga melakukan fungsi authentication dan charging.
SGSN – Serving GPRS Support Node
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) berperan sebagai pembawa data packets dari dan ke mobile station dalam geographical service area-nya. Fungsi lainnya adalah packet routing dan transfer, mobility management (attach/detach & location management), logical link management, dan authentication & charging. Location register SGSN menyimpan location information (misal, current cell, current VLR) dan user profiles (seperti, IMSI, address(es) digunakan di packet data network) dari semua user GPRS yang ter-register di SGSN ini.
Fungsi SGSN secara umum:
- Detunnel paket GTP dari GGSN (downlink)
- Tunnel paket IP menuju GGSN (uplink)
- Mobility management, standby mode mobile yang bergerak dari Routing Area ke Routing Area lain.
- Billing user data
Access Point
Sebuah access point adalah:
- Sebuah IP network yang memungkinkan sebuah mobile phone dapat terhubung
- Sebuah kumpulan settings yang digunakan untuk koneksi
- Opsi tertentu untuk setting di sebuah mobile phone
Ketika sebuah GPRS mobile phone “set up” PDP context, dipilih access point, yang dikenal sebagai Access Point Name (APN).
Contoh: flextronics.mnc012.mcc345.gprs.
Contoh: internet
Contoh: mywap
Access point ini kemudian digunakan untuk query DNS ke private DNS network. Akhir dari proses ini (disebut APN resolution) GGSN memberikan IP address dan menservis access point. Sehinga PDP context dapat diaktifkan.
PDP Context
PDP context adalah data terstruktur yang terdapat di SGSN dan GGSN yang berisi “subscriber’s session information” ketika subscriber memiliki “active session”. Bila sebuah mobile phone ingin menggunakan GPRS, pertama kali harus “attach” dan kemudian mengaktifkan PDP context. Alokasi PDP context data structure di SGSN menyatakan bahwa subscriber sedang terhubung dan GGSN menservis subscribers access point. Data yang tersimpan berisi:
IP address Subscribers
IMSI Subscribers
Subscribers
- Tunnel ID (TEID) di GGSN
- Tunnel ID (TEID) di SGSN
Tunnel ID (TEID) adalah nomor yang dialokasikan oleh GSN menyangkut data yang ditunnel untuk PDP context tertentu.
Terdapat 2 jenis PDP contexts:
Primary PDP Context
– Mempunyai unique IP addressSecondary PDP Context
-“Share” IP address dengan PDP context lainnya,
-Dibuat berdasarkan PDP context existing (untuk men-share IP address)
-Secondary PDP contexts bisa mempunyai Quality Of Service setting yang berbeda
A total of 11 PDP contexts (with any combination of Primary and Secondary) can co-exist.
Interfaces in the GPRS network
Gb – Interface between the Base Station Subsystem and the SGSN the transmission protocol could be Frame Relay or IP.
Gn – IP Based interface between SGSN and other SGSNs and (internal) GGSNs. DNS also shares this interface. Uses the GTP Protocol.
Gp – IP Based interface between internal SGSN and external GGSNs. Between the SGSN and the external GGSN, there is the Border Gateway (which is essentially a firewall). Also uses the GTP Protocol.
Ga – The interface servers the CDRs (Accounting records) which are written in the GSN and sent to the CG (Charging Gateway). This interface uses an GTP Protocol, with extensions that supports CDRs (Called GTP’ or GTP prime).
Gr – Interface between the SGSN and the HLR. Messages going through this interface uses the MAP3 Protocol.
Gd – Interface between the SGSN and the SMS Gateway. Can use MAP1, MAP2 or MAP3.
Gs – Interface between the SGSN and the MSC (VLR). Uses the BSSAP+ Protocol. This interface allows paging and station availability when it performs data transfer. When the station is attached to the GPRS network, the SGSN keeps track of which RA (Routing Area) the station is attached to. An RA is a part of a larger LA (Location Area). When a station is paged this information is used to conserve network resources. When the station performs a PDP Context, the SGSN has the exact BTS the station is using.
Gi – The interface between the GGSN and other external networks (Internet/WAP). Uses the IP protocol.
Ge – The interface between the SGSN and the SCP (Service Control Point). Uses the CAP Protocol.
Gx – The on-line policy interface between the GGSN and the CRF (Charging Rules Function). It is used for provisioning service data flow based charging rules. Uses the Diameter Protocol.
Gy – The on-line charging interface between the GGSN and the OCS (Online Charging System). Uses the Diameter Protocol (DCCA application).
Gz – The off-line charging interface between the GSN and the CG (Charging Gateway). Uses the CDRs (Accounting records).


Hebat nih Mudji skill or knowledgenya update terus , jangan lupa ngajak 2x yaa …
TOP BGT
Biasa aja frend, kita harus belajar terus, karena berpacu dengan waktu…
“Keep in touch”
capture juga ah, btw kalo boleh request ttg VPLS vs MPLS .. hehehehe
Mas Muji.. kalo punya MPLS ama VPLS yang lengkap bisa nda dikirim imel ke sahaya? Butuh bgt soalle… hohoho situs ini termasuk salah satu situs favorit saya.. isinya… mantappp.. Thx ya Mas Muji buau Ilmu2nya yang di share…
Halo mas Muji salam kenal………Keren lengkap Tertarik tuch tentang VPLS vs MPLS bisa minta tolong, tolong kirim email juga donk ttng VPLS vs MPLS…. terimakasih…….
DY,
Untuk lebih lengkapnya bisa dibaca di
http://cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk436/tk891/technologies_white_paper09186a00801f6084.shtml
Maklum belum sempat terjemahin….
Thanks
Assalamu’alaikum wr.wb.
Thanks bgt tuk mas Mudji tuk sharing ilmunya disini.Terutama ksmptn tuk anak komdat yg ingin gabung di operator seluler akibat migrasi 2G ke 3G nya…he..he..
Wa’alaikum salam ww
OK, No problem my friend.
Anda pasti bisa, gak beda jauh kok antara IP Core di GSM ama di KomDat, kan sama2 IP-Based.
Thanks
Lam kenal Mas… Thx for ilmunya..
Btw mo nanya dong bagaimana penjelasannya jika terjadi kendala koneksi pada pdp context di kaitkan dengan service session duration based…
Thx. mas atas pencerahannya…
Dear Ilham,
Mungkin bisa diperjelas tentang kendala koneksinya.
pemilihan service tergantung pada handset kita, memilih utk di set ke service duration atau volume based, bergantung pada APN.
Salam
Mudji
wah bagus pak artikelnya
dioperator mana pak kerjanya..hehehehe
salam kenal pak